
Machine Learning Demonstrator –Enhancing Data Usability with AI-based Multi-Model Data Fusion for DestinE
Enhancing data usability with AI-based Multi Model Data Fusion
Main contractor: Deutscher Wetterdienst DWD (German Meteorological Service)
What is it? Combining the capabilities of the Destination Earth digital twin infrastructure and the EuroHPC ecosystem, DWD will develop and demonstrate a machine learning system designed to integrate multiple model outputs into a single, optimised product.
Concrete applications examples:
The solution will overcome the limitations of individual models through their fusion, resulting in more reliable and accurate weather data supporting enhanced decision-making. The benefit will be demonstrated for selected sector-specific use cases (renewable energy, wildfires and agriculture).
Main target end users:
Meteorological services and decision-makers in different sectoral domains, including energy operators, civil protection and agriculture.
Machine learning to optimally merge forecasts from multiple models
For this Machine-Learning Demonstrator of Destination Earth DWD has gathered a team including Italy’s high performance computing centre Cineca, the Italian Agenzia ItaliaMeteo and the CIMA Foundation (Competence Centre of the Italian Civil Protection System for the hydrometeorological sector and disaster risk mitigation), gathering expertise in machine learning, weather forecasting and HPC integration.
As extreme weather events become more frequent and severe, DWD aims to leverage DestinE digital twins, the supercomputing capabilities provided by EuroHPC Joint Undertaking and existing operational prediction capabilities to derive enhanced extreme events information. Windstorms, heat waves, and wildfires are some examples of extreme events for which enhanced predictions could reduce the societal and economic impacts.
While traditional numerical weather prediction (NWP) models are highly advanced, they can struggle to capture small-scale processes. In particular, processes close to the surface remain difficult to represent, yet they are essential for predicting the impacts and taking actions at the local level.
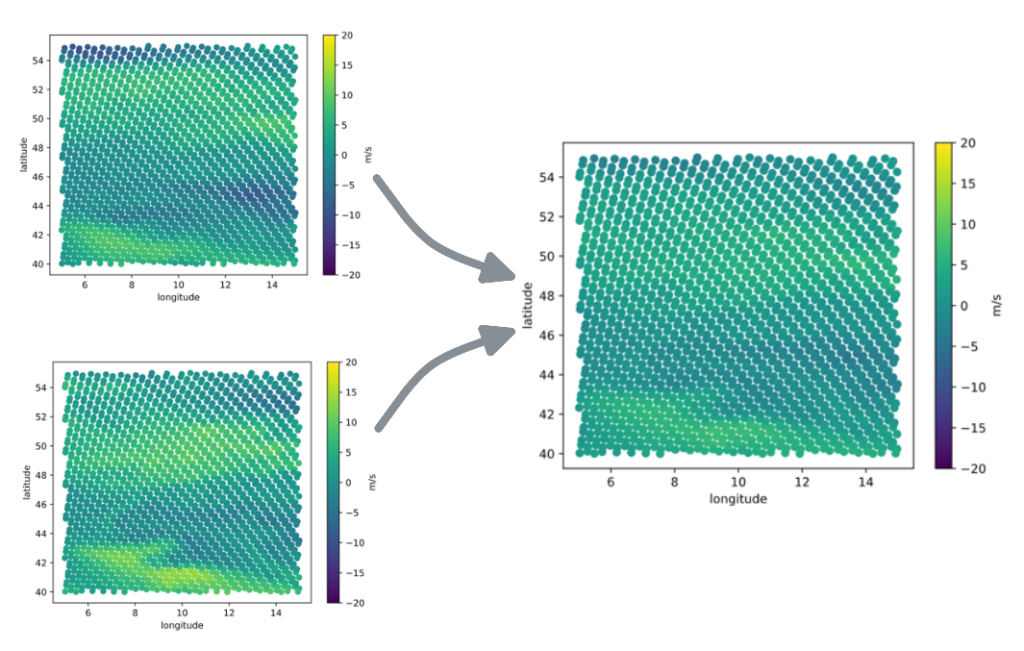
DWD will adapt its SynCast system, an advanced ML-based tool initially designed for data assimilation but adapted to produce merged NWP forecasts. SynCast is able to dynamically leverage the respective strengths of different model outputs while mitigating their inherent weaknesses (bias and others), resulting in a more reliable product for enhanced decision making.
SynCast will use inputs from the DestinE digital twins and other existing operational forecasts, such as ECMWF’s IFS and DWD’s ICON, and other national models. The SynCast neural network will process the different inputs using performance parameters to rank the inputs and produce actionable high-resolution forecasts for variables oriented for some of the sectors most impacted by climate change and weather extremes. The demonstrator will focus on wind, temperature and humidity, and will test the use of precipitation because of the critical importance of these variables for the case studies selected for the service such as renewable energy, agriculture and disaster management.
ECMWF, as a key implementing entity of the Destination Earth initiative of the European Union, has issued a series of pilot services contracts that demonstrate the added value of the Weather-Induced Extremes Digital Twin and the Climate Change Adaptation Digital Twin, and the wider DestinE architecture. The key target users of the pilot services are the sectors most impacted by climate change and weather extremes, ranging from maritime operations, coastal areas, energy and more. The contracts, reflecting the co-design strategy at the heart of DestinE, include a specific call for machine learning and artificial intelligence-based proposals as a part of the impulse to ML/AI techniques within Destination Earth led by the European Commission’s DG CNECT.